Car accidents are sudden, traumatic events that can result in a wide range of injuries, with neck injuries being among the most common and potentially debilitating. With its complex structure of bones, muscles, ligaments, and nerves, the neck is particularly vulnerable to the forces exerted during a collision. Various types of neck injuries that can occur in a car accident are crucial for recognizing symptoms and seeking timely medical treatment.
What Is A Neck Injury?
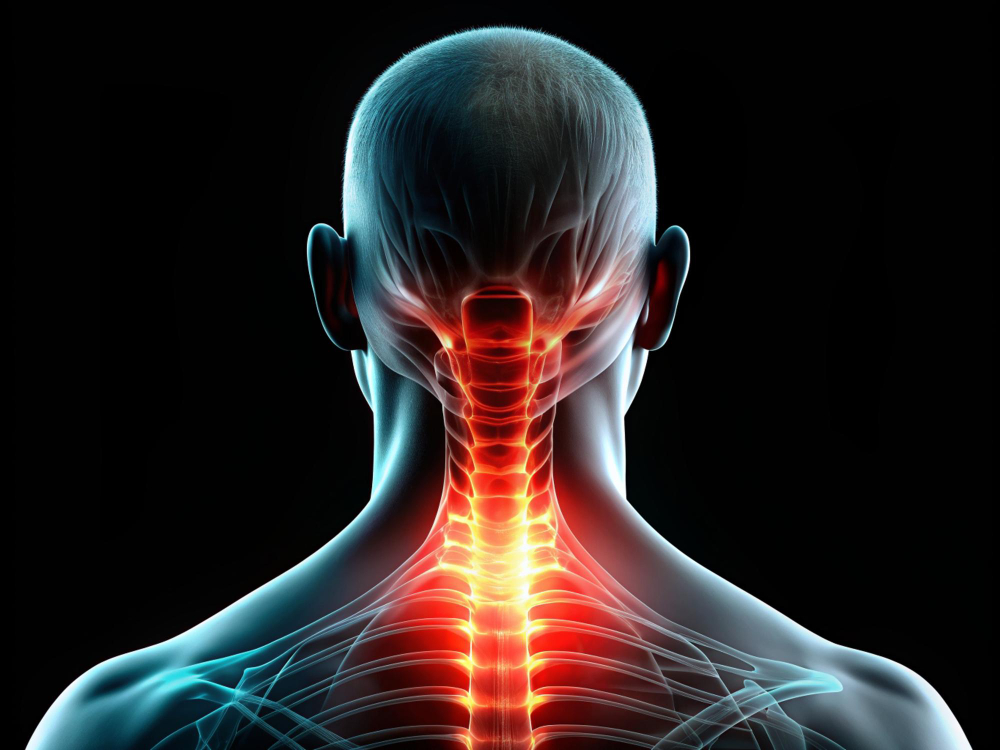
A neck injury refers to any damage or trauma to the structures within the neck, including the muscles, ligaments, bones (cervical vertebrae), nerves, and intervertebral discs. The neck, also known as the cervical spine, is a delicate and complex part of the body that supports the head’s weight and allows for a wide range of motion. Because of its flexibility and critical structures, the neck is particularly vulnerable to injuries, which can result from various causes such as accidents, falls, sports activities, or degenerative conditions.
Parts Of The Neck
The neck, also known as the cervical spine, is a vital and complex part of the body that connects the head to the torso.
It consists of several important structures and areas:
Vertebrae: The neck is made up of seven cervical vertebrae (C1 to C7), which are smaller and more flexible than other spinal vertebrae. These bones provide support and protection for the spinal cord and nerves.
Muscles: Numerous muscles surround and support the neck, facilitating movement and stability.
These include:
- Sternocleidomastoid: Located on the sides of the neck, it helps rotate and flex the neck.
- Trapezius: Large muscles that extend from the back of the head down to the shoulders and upper back, supporting the neck and shoulders.
- Scalene muscles: Found on the sides of the neck, they assist in neck and shoulder movements.
- Ligaments: Strong bands of connective tissue that connect bones to bones, providing stability and preventing excessive movement.
Intervertebral Discs: Situated between each cervical vertebra, these discs act as shock absorbers and allow for flexibility and movement of the neck.
Nerves: The cervical spine houses and protects the spinal cord, which extends from the brain down through the vertebrae. Spinal nerves branch out from the spinal cord through openings in the vertebrae, transmitting signals between the brain and the body.
Blood Vessels: The neck contains major blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain and head, including the carotid arteries and jugular veins.
Common Types Of Neck Injuries From Car Accidents
Neck injuries can vary widely in severity, from minor strains and sprains to serious fractures and spinal cord injuries.
Major Neck Injuries From Car Accidents
Cervical Fracture
A cervical fracture, commonly known as a broken neck, is a serious injury that involves a break in one or more of the cervical vertebrae—the bones that make up the neck portion of the spine. This type of injury is often caused by high-impact trauma, such as that from a car accident, sports injury, fall, or other significant force.
Causes
- Car Accidents: Sudden deceleration or direct impact can exert excessive force on the neck, leading to fractures.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports or activities with a high risk of falls (e.g., football, gymnastics) can result in cervical fractures.
- Falls: A fall from a significant height or onto a hard surface can cause fractures in the cervical spine.
- Violent Trauma: Incidents such as physical assault or accidents involving heavy objects falling onto the neck can also cause fractures.
Symptoms
- Severe Neck Pain: Persistent and intense pain at the site of the fracture.
- Swelling and Bruising: Noticeable swelling and discoloration around the neck area.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty moving the neck or head due to pain and instability.
- Neurological Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs, indicating potential nerve damage.
- Paralysis: In severe cases, loss of movement or sensation below the level of the injury, can indicate spinal cord involvement.
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is a severe and potentially life-altering condition resulting from damage to the spinal cord. This type of injury can disrupt communication between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to loss of movement, sensation, and various bodily functions below the site of the injury. Spinal cord injuries often result from significant trauma, such as that experienced in a car accident.
Causes
- Car Accidents: Sudden, forceful impacts can cause the spinal cord to be compressed, stretched, or severed.
- Falls: High falls or falls onto hard surfaces can lead to significant spinal cord damage.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports and activities with a high risk of falls or collisions can result in SCIs.
- Violence: Gunshot wounds, stab injuries, and other forms of physical assault can damage the spinal cord.
- Medical Conditions: Diseases such as tumors, infections, or degenerative conditions can also lead to spinal cord injuries.
Symptoms
- Loss of Movement: Partial or complete paralysis below the level of the injury.
- Loss of Sensation: Inability to feel touch, heat, cold, or pain below the injury site.
- Altered Sensation: Numbness, tingling, or burning sensations.
- Difficulty Breathing: Respiratory problems, particularly if the injury is in the cervical spine.
- Loss of Bladder and Bowel Control: Inability to control urinary or bowel functions.
- Spasms and Reflex Changes: Involuntary muscle movements or exaggerated reflexes.
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a common injury that can occur in the cervical spine (neck region) following a car accident or trauma. The intervertebral discs act as cushions between the vertebrae, providing flexibility and shock absorption. When a disc herniates, the soft inner material (nucleus pulposus) protrudes through a tear in the tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus), often irritating nearby nerves.
Causes
- Trauma: Sudden, forceful impacts or twisting motions during a car accident can cause a disc to herniate.
- Degenerative Changes: Wear and tear over time can weaken the discs, making them more susceptible to herniation.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities or occupations that involve repetitive lifting, bending, or twisting motions can contribute to disc herniation.
Symptoms
- Neck Pain: Often localized to the affected disc level, which may worsen with movement or certain positions.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that extends from the neck into the shoulders, arms, hands, or fingers, following the path of the affected nerve.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or pins-and-needles in the shoulders, arms, or hands.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles of the arms or hands, making it difficult to perform daily tasks.
Cervical Dislocation
Cervical dislocation refers to the displacement of one or more cervical vertebrae from their normal alignment, typically due to severe trauma or injury. This condition is serious and can result in spinal instability and potential damage to the spinal cord and surrounding structures.
Causes
- Trauma: High-impact collisions, such as car accidents or falls from heights, can exert enough force to dislocate cervical vertebrae.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports or activities that involve sudden, forceful movements of the neck can also cause cervical dislocation.
- +Violent Trauma: Physical assaults or accidents involving significant blunt force trauma to the neck area.
Symptoms
- Severe Neck Pain: Intense pain at the site of dislocation, often worsened by movement.
- Swelling and Bruising: Visible swelling and bruising around the neck area.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the neck or head due to instability.
- Neurological Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs, indicating potential nerve damage.
- Paralysis: In severe cases, loss of movement or sensation below the level of the dislocation, suggests spinal cord involvement.

Minor Neck Injuries From Car Accidents
Whiplash
Whiplash is a soft tissue injury that occurs when the neck is suddenly and forcefully jerked back and forth, resembling the cracking of a whip. This rapid movement can happen during rear-end collisions or other accidents that cause a sudden acceleration-deceleration force on the neck.
Symptoms:
- Neck Pain and Stiffness: The most common symptoms, often appear within 24 hours after the accident.
- Headaches: Typically originating from the base of the skull.
- Dizziness and Fatigue: Often accompanied by difficulty concentrating.
- Shoulder or Upper Back Pain: Due to the impact on surrounding muscles and ligaments.
- Numbness or Tingling: Occasionally felt in the arms.
Neck Strain
Neck strain, also known as a cervical strain, is a common injury that occurs when the muscles or tendons in the neck are stretched or torn due to sudden or excessive movement. This type of injury can result from car accidents, falls, sports injuries, or improper lifting techniques.
Causes:
- Sudden Impact: Such as in car accidents or sports collisions.
- Overuse: Repetitive motions or prolonged poor posture.
Symptoms:
- Neck Pain: Often localized and worsened with movement.
- Stiffness: Difficulty turning the head or tilting it sideways.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary muscle contractions that can cause further discomfort.
- Tenderness: Sensitivity to touch over the affected area.
Neck Sprain
A neck sprain occurs when the ligaments in the neck are stretched or torn, often due to sudden movements or impacts, such as those experienced in car accidents or sports injuries.
Causes:
- Accidents: Sudden jolts or impacts that force the neck beyond its normal range of motion.
- Sports Injuries: Collisions or falls that strain the neck ligaments.
- Poor Posture: Prolonged positions that strain the neck muscles and ligaments.
Symptoms:
- Neck Pain: Typically worsened with movement or palpation.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the neck freely.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the affected area.
- Muscle Spasms: Tightness or involuntary muscle contractions.
- Headaches: Especially originating from the base of the skull.
Facet Joint Injury
Facet joint injuries involve damage to the small joints located between and behind adjacent vertebrae in the spine. These joints play a crucial role in allowing the spine to bend and twist. During a car accident, sudden impacts or whiplash-like motions can strain or injure these joints, leading to significant discomfort and reduced mobility.
Symptoms:
- Neck Pain: Typically worsens with movement or certain positions.
- Stiffness: Difficulty with bending or turning the neck.
- Radiating Pain: Can extend into the shoulders or upper back.
- Headaches: Often originating from the base of the skull.
- Muscle Spasms: Tightness and involuntary contractions in the surrounding muscles.
Minor Soft Tissue Injuries
Minor soft tissue injuries in the neck are common occurrences in car accidents, typically resulting from sudden movements or impacts. These injuries affect the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the neck and are generally less severe compared to fractures or spinal cord injuries.
Symptoms:
- Pain and Tenderness: In the neck area, often localized to specific muscles or ligaments.
- Swelling: Around the affected area due to inflammation.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the neck, especially after the accident.
- Bruising: Visible discoloration of the skin in some cases.
How To Treat Neck Pain After An Auto Accident?
Treating neck pain after an auto accident involves several approaches aimed at reducing pain, promoting healing, and restoring normal function.
Here are some common treatments and strategies:
1. Medical Evaluation
Seek medical evaluation promptly after the accident, even if neck pain seems mild initially. A healthcare professional can assess the extent of the injury and recommend appropriate treatment.
2. Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the neck initially can help reduce inflammation and pain. Avoid activities that exacerbate pain or strain the neck further. Gradually resume normal activities as pain improves.
3. Medication
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: These may be prescribed to alleviate muscle spasms if they are contributing to neck pain.
4. Ice and Heat Therapy
- Ice Packs: Apply ice packs to the neck for 15-20 minutes several times a day during the first 48 hours after the injury to reduce swelling and pain.
- Heat Therapy: After the initial acute phase, applying heat (warm showers, heating pads) can help relax muscles and improve circulation.
5. Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design exercises and stretches to strengthen neck muscles, improve range of motion, and promote healing. Manual therapy techniques may also be used to alleviate muscle tension and improve flexibility.
6. Neck Braces or Collars
In some cases, a neck brace or collar may be recommended to provide support and limit neck movement while the tissues heal. However, prolonged use of a collar is generally discouraged as it can lead to muscle weakening.
7. Epidural Steroid Injections
For severe pain that does not respond to conservative treatments, corticosteroid injections may be administered into the epidural space around the spinal cord to reduce inflammation and pain.
8. Alternative Therapies
- Massage Therapy: Gentle massage can help relax tense muscles and improve circulation.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese therapy involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain and promote healing.
9. Education and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Posture Correction: Maintaining good posture can reduce strain on the neck. Ergonomic adjustments at work or while driving can also help.
- Sleep Position: Use a supportive pillow and maintain a neutral spine position while sleeping to avoid exacerbating neck pain.
10. Psychological Support
In cases of chronic neck pain or significant emotional distress following the accident, counseling or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may be beneficial to address psychological factors contributing to pain.
FAQs
What is whiplash?
Whiplash is a neck injury caused by a sudden back-and-forth movement of the neck, commonly occurring in car accidents. It can cause pain, stiffness, and other symptoms.
What are the symptoms of a cervical fracture?
Symptoms include severe neck pain, swelling, tenderness, and possible loss of sensation or movement in the arms or legs.
How do I know if I have a herniated disc in my neck?
Symptoms may include neck pain, radiating pain into the shoulders or arms, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or hands.
What should I do immediately after a car accident if I suspect a neck injury?
Seek medical attention promptly. Avoid moving unnecessarily and follow any instructions from emergency responders.
How are neck injuries diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests (such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI), and evaluation of symptoms and medical history.
Seeking For Help. Contact Us Our Accidental Lawyer
If you’ve been involved in a car accident and need legal assistance, contacting a car accident lawyer can provide invaluable support and guidance. A skilled lawyer specializing in car accidents can help you navigate the complexities of insurance claims, assess liability, negotiate settlements, and represent your interests in court if necessary. Consulting with a car accident lawyer early in the process can help alleviate stress and maximize your chances of a favorable outcome.
Interesting Reads:
Common Brain Injuries By Car Accidents






